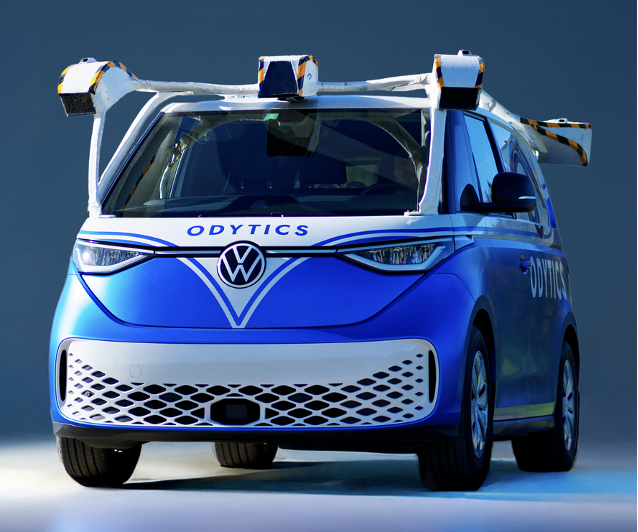
The main objective of the project is to accelerate the adoption of artificial intelligence in the digital transition of Swiss SMEs. The associated socio-economic challenge is to increase their competitiveness, to limit relocation and to create new competences at the interface of laboratories and the practical use of artificial intelligence.

This project aims to develop a Swiss carbon performance framework to address gaps in Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) for buildings by standardizing assessment, reporting, and data exchange, while promoting transparency and collaboration between stakeholders, public authorities, and certification bodies.

EVAL2Rn is a digital tool for assessing the risk related to the presence of radon before building construction and renovation. It will be based on a mix of statistical and AI models to predict at scale the radon presence risk.

Artificial Intelligence's main purpose is to augment the capacities of the humans, which raises questions how to build secured, sustainable, adequate interfaces between AI and humans. iCoSys is member of SCAI, a national competence center for the development and democratization of augmented intelligence.

The A3P FNS Bridge project aims at developing novel photo-voltaic materials based on perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells. Our aim is to build AI tools to accelerate the research including image analysis and optimal process parameter discovery.

In the AD-DITION innosuisse project, our goal is to offer end-to-end creation of dynamic and contextual ads using AI. Ads should become more informative by linking to external context and also adapt its content according to user engagement.
RESOUND aims to be the first-of-its-kind to provide a higher standard of information quality that involves the joint learning of trust and forecasting models.

This project advances video analysis with AI-driven real-time event detection and intelligent forensic search capabilities.

The Digital Human Twin (DHT) project creates digital replicas of health conditions to support personalized treatment, clinical trials, and surgical planning, aligning with Switzerland's healthcare priorities.
At iCoSys Fribourg, we ave set up a microservice cluster to deploy machine learning models scheduled by Kubernetes, including shared GPU support for deep learning.

In this project, we explore how AI can augment art, making it interactive and surprising. Specific creations were developed and showcased in the context of the Light Festival of Murten and other artistic shows.
The aim of i2b's living laboratory project, "Infrastructures to Blind", is to develop prototypes for an inclusive ecosystem to improve mobility in public spaces and buildings for the visually impaired. The prototypes are both digital and physical, so that people who do not have or are not familiar with a smartphone can also benefit from the project.
Rapid analysis of building stock by AI and expert systems to estimate their energy and structural performance in order to define appropriate remediation strategies with a favorable carbon balance.
Innosuisse project to research predictive maintenance approaches on combustion engines from Liebherr.
FomoTSF explores the possibilities to use foundation models for time-series forecasting.

The primary goal of the project 'BeCool: Human-in-the-loop Heating Control System Validation' is to validate innovative heating control systems that integrate user feedback to reduce energy consumption while ensuring occupant comfort. This initiative, supported by Smart Living Lab, aims to enhance building sustainability, optimize energy usage, and validate user-centric heating regulation strategies.

Hestia brings technological resources within nursing homes, personal homes or protected apartments in order to improve the life comfort of vulnerable people and the working conditions of their medical staff.
In the Innosuisse project "Smart Learning in the Digital Era" (SLIDE), we aim to create a learning platform that allows each person to create his or her own knowledge representation in a very personal way for teaching and learning.

Partially sighted persons are daily struggling in non-codified situations where objects are new or at unexpected location. This project aims to put the latest AI findings (Zero-shot object discovery and finding) at the service of these people in such a way they can carry out their daily tasks with less dependency on other persons.
ModIA creates digital twins using a hybrid approach of machine learning and physics

"El Diango" project tackles Swiss electrical grid strain by optimizing electricity usage in Fribourg's HEIA-FR. It identifies waste areas, enhances energy efficiency, and lays groundwork for future initiatives.

The goal of the DiagnoBat is to create an AI-driven platform dedicated to monitoring building and establish diagnostics. It integrates new data capture and visualization solutions, along with the latest AI advances for signal analysis.

DigiRENT-AI aims to add AI to IMMOMIG SA's DigiRENT service for the digital management of rental properties, in order to automate certain steps by predicting e.g. the best publication strategies, the most suitable agencies to rent a property or the best applications.
The AII4.0 project aims at developing standardized, universal, scalable and affordable AI solutions for predictive maintenance in the context of manufacturing Industries. Real-life use cases and specifications will be defined with the help of industries in order to validate the development.

In this project, we develop novel methods for handwriting recognition in historical documents to improve recognition accuracy, especially for the challenging case of non-frequent writers with only few letters in the dataset.

In this study we analyse video data from Swiss highways with custom object detection models to identify the types of trucks on a certain highway strip. A custom dataset has been created to train and evaluate ML models. YOLO performs well and gives very interesting classification results despite the presence of several challenges like motion, shadow and inter-class similarity.

The project aims to implement methods for evaluating and optimizing the energy and environmental impact of applications based on artificial intelligence models with a view to creating a new center of expertise in Sustainable AI.
RMS brings technological resources within nursing homes, personal homes or protected apartments in order to improve the life comfort of vulnerable people and the working conditions of their medical staff.
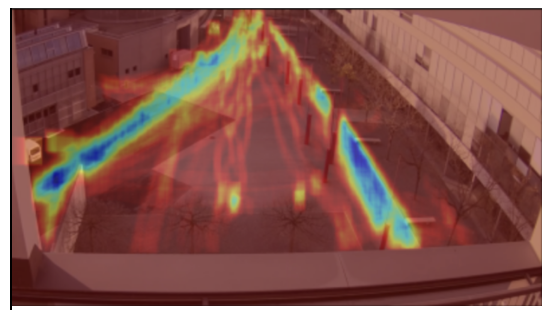
The goal of the Greenum project is to use a camera and image analysis models to study the flow of movement in a given space.
PeNoBe (Peak Noise Behaviour) studies the classification of vehicles into electric, gasoline and hybrid classes.
Rapid analysis of building stock by AI and expert systems to estimate their energy and structural performance in order to define appropriate remediation strategies with a favorable carbon balance.

Project to improve DNA sequence analysis using machine learning to predict sequencing artefacts with Phenosystems SA as the industrial partner.
Detect and predict anomalies in high performance electrical transfomers
Innosuisse project using machine learning to develop a sommelier in your pocket
Innosuisse project developing a personalized meeting assistant based on LLM technologies with the startup Wedo, based in Fribourg

The purpose of the Datalambic Project is to create a tool ecosystem for semi-automated collection, preparation and correction of high-quality data in order to (re)train neural translation engines in the desired specialization(s), including looped feedback from linguists, lawyers and users.

LYSR is a startup founded by members of iCoSys in the context of a SwissUniversities startup accelerator program. LYSR focuses on one of the key strengths of iCoSys, which is anomaly detection and predictive maintenance in time-series data for industry 4.0.
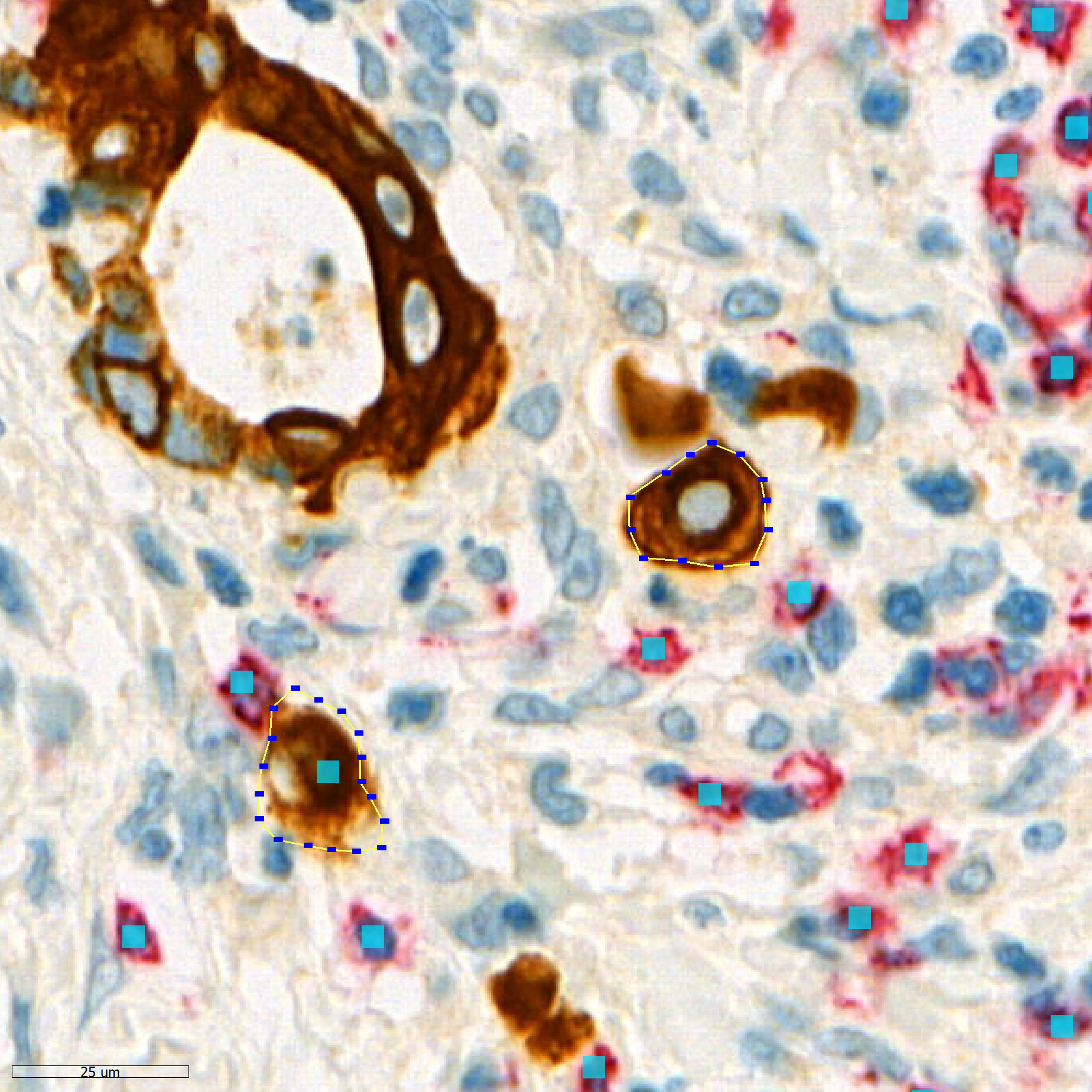
In this project, we are developing geometric deep learning methods to support pathologists in the diagnostic process. Specifically, we are looking at tumor buds and lymphocytes in colorectal cancer and their spatial relationship.

SwissTranslation aims to develop novel methods for automatic translation from Swiss German to High German that are able to cope with a lack of large text corpora.

The European project BIOSMART aims to develop active and smart bio-based and compostable packages that make possible: light weighting, reduced food residues, shelf life monitoring, longer shelf life and easier consumer waste handling.

In the context of Facility 4.0, we will study the optimization of buildings energy consumption hand in hand with our partners. This will allow us to focus on real world anomalies in the vast amount of data at our disposal; thanks to our BBData infrastructure.

In this thesis, we would like to explore the possibilities of machine learning techniques to detect anomalies in time-series data.
In an international industrial research project we apply the latest technologies in machine learning to do handwriting recognition in tax forms.

Development of a computer-based support for linking actors in the Alpine Space and create new value chains in the bio-based economy. Technologies such as crawling, NLP and graph representations are used in this project. The project was later renamed to DeepVCG and resulted in a spinoff called vcg.ai.

The AINews project aims to provide intelligent conversational agent technologies that support the digital transformation of the press. These technologies will help make the information channel dynamic through dialogues, retain readers through content customization and optimize editorial directions through maps of interests on common topics.
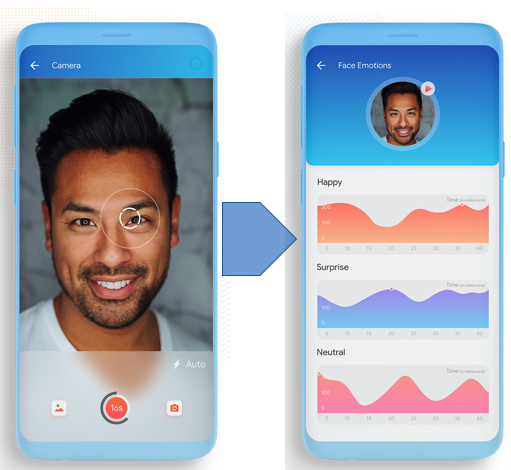
ADVANCe is an Innosuisse funded project that focuses on the analysis of emotions and their congruence in video feeds. We partner in this project with IDIAP (Martigny) and CM Profiling (Bern).

Information and communications technologies are central tools for Humanitarian Organizations operations. The ICT specialist training is designed to help them achieve their missions in the safest and most efficiently way. We propose a tailored training based on educational innovation tools.

BBDATA stands for Big Building Data and aims at developing a scalable cloud platform and tools for storing and processing smart building data. The services are targeting data access, processing and analysis, using open, robust, standardized and secured big data technologies.
DLL is a machine learning framework that aims to provide a C++ implementation of neural networks and convolutional neural networks. The implementation provides significant speedups on cpu in comparison to other frameworks such as TensorFlow or Torch. It is then dedicated to the use phase of such deep models where performance on cpu is requested, such as in industry 4.0 applications.

The CityPulse project aims to offer a live, localized and continuous measurement of the city through the installation of a network of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors.
In this project, iCoSys is specifically interested in the analysis and development of versatile approaches for the detection of abnormal events using machine learning approaches (WP5).

With more than 500K sentences gathered from the internet, SwissCrawl is the most comprehensive corpus of Swiss German sentences to date. It was created as part of the SwissTranslation project, in partenariat with Swisscom.
Optisoil is a project that leverages machine learning to speed up numerical simulations in the domain of civil engineering.

COJAC is a two-fold tool for Java. It provides a numerical sniffer that detects anomalies arising in arithmetic operations and an enriching wrapper that automatically converts every float/double data into richer number types. With COJAC you don't have to modify your source code or even recompile. All the work is done at runtime, when your application gets instrumented on-the-fly. Feel free to browse the source code at https://github.com/Cojac.

This thesis by Oussama Zayene aims to contribute to the current research in the field of Video Optical Character Recognition (OCR) by developing novel approaches that automatically detect and recognize embedded Arabic text in news videos.

TFC is a distributed application development framework, based on POP-Java. It allows developers to develop decentralized applications in which the users can share computing power and data in a secure manner.
The connection between the different users of the software is made in a way similar to social networks, allowing users to create communities around certain applications.
ETL is a header only library for C++ that provides vector and matrix classes with support for Expression Templates to perform very efficient operations on them.

Process4Plastics (P4P) aims to build a dedicated methodology of process engineering for the production of plastics parts. In the industry 4.0 era, machines will be equipped with many sensors and actuators and be connected together to create intelligent networks.

The availability of low-cost sensors covering a whole city offers new perspectives in terms of research and development. Urban Pulse aims at offering an integrated solution allowing capture, storage and processing of urban signals to the iNUIT program and HES-SO researchers.

DAPLAB aims at facilitating the access for enterprises and universities to emerging technologies in the area of big data and intelligent data analysis by managing an infrastructure composed of cluster of servers dedicated to storage and computation, to which universities and local companies will have access.

This thesis of Baptiste Wicht investigates the use of Deep Learning feature extraction for image processing tasks. The goal being to see if these features are able to outperform hand-crafted features and how difficult it is to generate such features.

In this PhD thesis by Beat Wolf, a graphical data analysis pipeline has been developed to make the analysis of genetic data easier in a diagnostics environment. Intuitive graphical user-interfaces as well as optimized algorithms have been developed to alllow geneticists to perform the data analysis even on off the shelf hardware. We also developed a distributed programming language called POP-Java to make the development of distributed algorithms easier.

PhD Thesis by Christophe Gisler: time series represent a large part of the data supply worldwide and many data mining tasks, such as prediction and classification, are concerned with them. This thesis focused on the analysis and development of generic machine learning approaches to multivariate time series classification.
A dataset of 160 pictures of Sudoku taken in various newspapers using smartphone Cameras. The dataset is divided into two sets: 120 training images and 40 test images.

Tactical Ad-hoc networK Emulation aims to conceive, develop and implement algorithms to deploy reliable tactical applications over ad-hoc networks for Armasuisse.

POP-C++ is a comprehensive object-oriented system for developing HPC applications on the Grid. It consists of a programming suite (language, compiler) and a run-time system for running POP-C++ applications.

POP-Java is a Java implementation of the POP programming model. POP-Java allows programmers to easily distribute object orientated Java applications over the network, without having to handle the low level distribution work themselves. POP-Java is compatible with other implementations of the POP model, such as POP-C++, allowing “mixed” applications to be written.

PhD thesis of Lu Yao - Overhigh data redundancy and communication load are the most conventional challenges for the constrained resources of wireless sensors. How to efficiently transport the designated sensor readings from source nodes to sink nodes by using in-network data aggregation functions is the most important issue concerned in this thesis. For the purpose of guiding the transmission direction of data messages, Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is embedded into the routing process.

SENSIMED AG has developed Triggerfish, a wearable non-invasive solution to monitor continuously intra-ocular pressure (IOP). The purpose of the Sensimed Diagnosis project is to analyze, design and implement signal processing, feature extraction and pattern recognition tools to exploit the signals monitored by the Triggerfish.

PhD thesis of Antonio Ridi: In this thesis we describe our work on the use of generative modeling for the classi
cation of time series in the context of in-home monitoring. More precisely, we use generative approaches as Gaussian Mixture models (GMMs) and Hidden Markov models (HMMs).

With a focus on complex systems, iCoSys approaches the different challenges of DNA analysis with its expertise in various techniques acquired in the different domains of computer science.

VideoProtector is an innovative solution to manage cameras streams in a central place. This centralization offers also the possibility to run incident detection algorithms in a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) mode.

PhD Thesis of Gérôme Bovet - The thesis is about the conception and implementation of a framework to develop dedicated smart buildings applications. By relying on Web technologies, we demonstrate the development of seamless services while reusing the available resources within the network. We also demonstrated in this thesis the exposure of machine learning services made accessible through Web interfaces and hiding the complexity of the process.

Thesis of Nayla Sokhn - Niche-Overlap graphs depict the competition between species in the nature. In this thesis, we explore these networks from three different perspective: algorithmic, structure and dynamics.

The iFloor project aims at developing intelligent floors able to detect, localize and track persons in indoors environment. It relies on low-cost sensors integrated in the material of the floor.

GreenMod aims at providing a framework easing the development of building management systems on top of Web technologies.

The idea of the project is to leverage on large sets of linguistic data and on machine learning algorithms able to discover automatically pronunciation rules. Such rules are then used in “symbolic mappers” able to transform a grapheme representation into a phonetic representation and to propose probable alterations of the pronunciation. The mappers are then used to propose clients with new domain names that sound similar to their original search.

This machine learning dataset contains electric consumption signatures of 225 appliances, spread into 15 categories and including 6 time series such as current, active power and reactive power. It also includes two test protocols to be used for appliance recognition tasks.

Low-cost charging station.
One of the goal of the ePark – Electric Park System project was to build a low-cost charging station offering similar functionalities but leveraging on the emergence of cheap machine-to-machine communication nodes.

ePark – Intelligent Parking System is a web service allowing drivers to be directed towards parking locations maximizing the probability to find a free parking space.

The ePark project has investigated ways to make the different charging station Information Systems interoperable (IS).

Swiss Academic Compute Cloud (SwissACC) is an short project which complement the SMSCG project. The project provides a range of services and know-how from over 10 AAA/SWITCH projects. The 14 SwissACC partners work on two main objectives: sustaining and preserving the research communities of the former AAA/SWITCH grid projects, and increasing user and usage numbers. The project focuses on consolidating the services and simplifying the procedures that have been created to support Swiss communities. Its main goal is to free researchers from complex computational aspects of their research so they can focus on their core work.

The first version of a database of appliance consumption signatures: 100 home appliances, 10 categories, 6 consumption measure types. It also includes two test protocols to be used for appliance recognition tasks.
The primary goal of the project SMSCG (Swiss Multi-Science Computing Grid) is to provide computational resources to solve scientific computational problems. This involves the installation, commissioning and operation of a computational grid across several institutions of the Swiss higher education sector with active involvement of applications from different scientific domains.

We all have been struggling to use a Linux machine at HEIA-FR because there is no official support for Linux machines...
So this page is for you to gain some time if you have questions about different Linux related configurations.