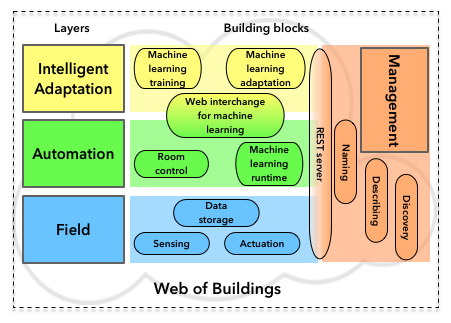
Buildings are increasingly equipped with dedicated automation networks, aiming to reduce the energy consumption and to optimize the comfort. On the other hand, we see the arrival of sensors and actuators related to the Internet of Things, which can naturally connect to IP networks. Due to constraints imposed by the obsolescence or physical properties of buildings, it is not uncommon that different technologies have to coexist.
These networks operate with different models and protocols, making the development of global automation systems difficult. Traditional models of distributed systems are not adapted to the context of sensor networks. The paradigm of the Web of Things is resource-based and strives to standardize the application layer of different objects using Web technologies, primarily HTTP and REST.
In this thesis, we use the Web of Things to create a framework dedicated to smart buildings, allowing developers to compose applications without knowledge of the underlying technologies.
By relying on Web technologies, we demonstrate the development of seamless services while reusing the available resources within the network (sensors and actuators), forming a self-managed cloud. In order to equip the buildings with a higher-level intelligence, we also demonstrated in this thesis the exposure of machine learning services made accessible through Web interfaces and hiding the complexity of the process.
Publications
-
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet, G. Briard, and J. Hennebert, “A Scalable Cloud Storage for Sensor Networks,” in 4th Int. Conf. on Internet of Things. IoT 2014 MIT, MA, USA. Web of Things Workshop, 2014.
G. Bovet, G. Briard, and J. Hennebert, “A Scalable Cloud Storage for Sensor Networks,” in 4th Int. Conf. on Internet of Things. IoT 2014 MIT, MA, USA. Web of Things Workshop, 2014.
[Bibtex]@conference{bovet2014:wot2, author = "G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Gautier Briard and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "Data storage has become a major topic in sensor networks as large quantities of data need to be archived for future processing. In this paper, we present a cloud storage solution benefiting from the available memory on smart things becoming data nodes. In-network storage reduces the heavy traffic resulting of the transmission of all the data to an outside central sink. The system built on agents allows an autonomous management of the cloud and therefore requires no human in the loop. It also makes an intensive use of Web technologies to follow the clear trend of sensors adopting the Web-of-Things paradigm. Further, we make a performance evaluation demonstrating its suitability in building management systems.", booktitle = "4th Int. Conf. on Internet of Things. IoT 2014 MIT, MA, USA. Web of Things Workshop", doi = "10.1145/2684432.2684437", isbn = "978-1-4503-3066-4", keywords = "Distributed databases, cloud storage, web-of-things, sensor networks, internet-of-things", note = "Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", publisher = "ACM New York", series = "International Conference on the Internet of Things - IoT 2014", title = "{A} {S}calable {C}loud {S}torage for {S}ensor {N}etworks", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/wot-2014-a-scalable-cloud-storage-for-sensor-networks.pdf", year = "2014", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet, A. Ridi, and J. Hennebert, “Toward Web Enhanced Building Automation Systems – Big Data and Internet of Things: A Roadmap for Smart Environments,” , C. D. Nik Bessis, Ed., Springer, 2014, vol. 546, pp. 259-284.
G. Bovet, A. Ridi, and J. Hennebert, “Toward Web Enhanced Building Automation Systems – Big Data and Internet of Things: A Roadmap for Smart Environments,” , C. D. Nik Bessis, Ed., Springer, 2014, vol. 546, pp. 259-284.
[Bibtex]@inbook{bovet:2014:bookchap, Abstract = {The emerging concept of Smart Building relies on an intensive use of sensors and actuators and therefore appears, at first glance, to be a domain of predilection for the IoT. However, technology providers of building automation systems have been functioning, for a long time, with dedicated networks, communication protocols and APIs. Eventually, a mix of different technologies can even be present in a given building. IoT principles are now appearing in buildings as a way to simplify and standardise application development. Nevertheless, many issues remain due to this heterogeneity between existing installations and native IP devices that induces complexity and maintenance efforts of building management systems. A key success factor for the IoT adoption in Smart Buildings is to provide a loosely-coupled Web protocol stack allowing interoperation between all devices present in a building. We review in this chapter different strategies that are going in this direction. More specifically, we emphasise on several aspects issued from pervasive and ubiquitous computing like service discovery. Finally, making the assumption of seamless access to sensor data through IoT paradigms, we provide an overview of some of the most exciting enabling applications that rely on intelligent data analysis and machine learning for energy saving in buildings.}, Author = {G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Antonio Ridi and Jean Hennebert}, Chapter = {11}, Doi = {10.1007/978-3-319-05029-4_11}, Editor = {Nik Bessis, Ciprian Dobre}, Isbn = {9783319050287}, Keywords = {iot, wot, smart building}, Note = {http://www.springer.com/engineering/computational+intelligence+and+complexity/book/978-3-319-05028-7}, Pages = {259-284}, Publisher = {Springer}, Series = {Studies in Computational Intelligence}, Title = {{T}oward {W}eb {E}nhanced {B}uilding {A}utomation {S}ystems - {B}ig {D}ata and {I}nternet of {T}hings: {A} {R}oadmap for {S}mart {E}nvironments}, Pdf = {http://hennebert.org/download/publications/springer-2014_towards-web-enhanced-building-automation-systems.pdf}, Volume = {546}, Year = {2014}, Pdf = {http://hennebert.org/download/publications/springer-2014_towards-web-enhanced-building-automation-systems.pdf}, Bdsk-Url-2 = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-05029-4_11}} -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Will web technologies impact on building automation systems architecture?,” in International Workshop on Enabling ICT for Smart Buildings (ICT-SB 2014), 2014, pp. 985-990.
G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Will web technologies impact on building automation systems architecture?,” in International Workshop on Enabling ICT for Smart Buildings (ICT-SB 2014), 2014, pp. 985-990.
[Bibtex]@conference{bovet2014:ant, Abstract = {Optimizationffices, factories and even private housings are more and more endowed with building management systems (BMS) targeting an increase of comfort as well as lowering energy costs. This expansion is made possible by the progress realized in pervasive computing, providing small sized and affordable sensing devices. However, current BMS are often based on proprietary technologies, making their interoperability and evolution more didcult. For example, we observe the emergence of new applications based on intelligent data analysis able to compute more complex models about the use of the building. Such applications rely on heterogeneous sets of sensors, web data, user feedback and self-learning algorithms. In this position paper, we discuss the role of Web technologies for standardizing the application layer, and thus providing a framework for developing advanced building applications. We present our vision of TASSo, a layered Web model facing actual and future challenges for building management systems.}, Author = {G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Jean Hennebert}, Booktitle = {International Workshop on Enabling ICT for Smart Buildings (ICT-SB 2014)}, Doi = {10.1016/j.procs.2014.05.522}, Issn = {1877-0509}, Keywords = {Building Management System, Internet-of-Things, Web-of-Things, Architecture}, Note = {Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.}, Pages = {985-990}, Series = {Procedia Computer Science}, Title = {{W}ill web technologies impact on building automation systems architecture?}, Pdf = {http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/ant-procedia-2013-energy-efficient-optimization-layer-for-event-based-communications-on-wi-fi-things.pdf}, Volume = {32}, Year = {2014}, Pdf = {http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/ant-procedia-2013-energy-efficient-optimization-layer-for-event-based-communications-on-wi-fi-things.pdf}, Bdsk-Url-2 = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2014.05.522}} -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Distributed Semantic Discovery for Web-of-Things Enabled Smart Buildings,” in First International Workshop on Architectures and Technologies for Smart Cities, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2014, pp. 1-5.
G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Distributed Semantic Discovery for Web-of-Things Enabled Smart Buildings,” in First International Workshop on Architectures and Technologies for Smart Cities, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2014, pp. 1-5.
[Bibtex]@conference{bovet:ntms:2014, Abstract = {Nowadays, our surrounding environment is more and more scattered with various types of sensors. Due to their intrinsic properties and representation formats, they form small islands isolated from each other. In order to increase interoperability and release their full capabilities, we propose to represent devices descriptions including data and service invocation with a common model allowing to compose mashups of heterogeneous sensors. Pushing this paradigm further, we also propose to augment service descriptions with a discovery protocol easing automatic assimilation of knowledge. In this work, we describe the architecture supporting what can be called a Semantic Sensor Web-of-Things. As proof of concept, we apply our proposal to the domain of smart buildings, composing a novel ontology covering heterogeneous sensing, actuation and service invocation. Our architecture also emphasizes on the energetic aspect and is optimized for constrained environments.}, Address = {Dubai, United Arab Emirates}, Author = {G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Jean Hennebert}, Booktitle = {First International Workshop on Architectures and Technologies for Smart Cities}, Doi = {10.1109/NTMS.2014.6814015}, Editor = {Mohamad Badra; Omar Alfandi}, Isbn = {9781479932245}, Keywords = {Smart buildings, Discovery, Semantics, Ontologies}, Month = {Mar}, Pages = {1-5}, Publisher = {IEEE}, Title = {{D}istributed {S}emantic {D}iscovery for {W}eb-of-{T}hings {E}nabled {S}mart {B}uildings}, Pdf = {http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/ntms-2014-distributed-semantic-discovery-for-web-of-things-enabled-smart-buildings.pdf}, Year = {2014}, Pdf = {http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/ntms-2014-distributed-semantic-discovery-for-web-of-things-enabled-smart-buildings.pdf}, Bdsk-Url-2 = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/NTMS.2014.6814015}} -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet, G. Briard, and J. Hennebert, “A Scalable Cloud Storage for Sensor Networks,” in 4th Int. Conf. on Internet of Things. IoT 2014 MIT, MA, USA. Web of Things Workshop, 2014.
G. Bovet, G. Briard, and J. Hennebert, “A Scalable Cloud Storage for Sensor Networks,” in 4th Int. Conf. on Internet of Things. IoT 2014 MIT, MA, USA. Web of Things Workshop, 2014.
[Bibtex]@conference{bovet2014:wot2, Abstract = {Data storage has become a major topic in sensor networks as large quantities of data need to be archived for future processing. In this paper, we present a cloud storage solution bene ting from the available memory on smart things becoming data nodes. In-network storage reduces the heavy traffic resulting of the transmission of all the data to an outside central sink. The system built on agents allows an autonomous management of the cloud and therefore requires no human in the loop. It also makes an intensive use of Web technologies to follow the clear trend of sensors adopting the Web-of-Things paradigm. Further, we make a performance evaluation demonstrating its suitability in building management systems.}, Author = {G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Gautier Briard and Jean Hennebert}, Booktitle = {4th Int. Conf. on Internet of Things. IoT 2014 MIT, MA, USA. Web of Things Workshop}, Doi = {10.1145/2684432.2684437}, Isbn = {978-1-4503-3066-4}, Keywords = {Distributed databases, cloud storage, web-of-things, sensor networks, internet-of-things}, Note = {Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.}, Publisher = {ACM New York}, Series = {International Conference on the Internet of Things - IoT 2014}, Title = {{A} {S}calable {C}loud {S}torage for {S}ensor {N}etworks}, Pdf = {http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/wot-2014-a-scalable-cloud-storage-for-sensor-networks.pdf}, Year = {2014}, Pdf = {http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/wot-2014-a-scalable-cloud-storage-for-sensor-networks.pdf}, Bdsk-Url-2 = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2684432.2684437}} -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet, A. Ridi, and J. Hennebert, “Virtual Things for Machine Learning Applications:,” in Fifth International Workshop on the Web of Things – WoT 2014, 2014.
G. Bovet, A. Ridi, and J. Hennebert, “Virtual Things for Machine Learning Applications:,” in Fifth International Workshop on the Web of Things – WoT 2014, 2014.
[Bibtex]@conference{bovet2014:wot, Abstract = {Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices, especially sensors are producing large quantities of data that can be used for gathering knowledge. In this field, machine learning technologies are increasingly used to build versatile data-driven models. In this paper, we present a novel architecture able to execute machine learning algorithms within the sensor network, presenting advantages in terms of privacy and data transfer efficiency. We first argument that some classes of machine learning algorithms are compatible with this approach, namely based on the use of generative models that allow a distribution of the computation on a setof nodes. We then detail our architecture proposal, leveraging on the use of Web-of-Things technologies to ease integration into networks. The convergence of machine learning generative models and Web-of-Things paradigms leads us to the concept of virtual things exposing higher level knowledge by exploiting sensor data in the network. Finally, we demonstrate with a real scenario the feasibility and performances of our proposal.}, Author = {G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Antonio Ridi and Jean Hennebert}, Booktitle = {Fifth International Workshop on the Web of Things - WoT 2014}, Doi = {10.1145/2684432.2684434}, Isbn = {978-1-4503-3066-4}, Journal = {Fifth International Workshop on the Web of Things (WoT 2014)}, Keywords = {Machine learning, Sensor network, Web-of-Things, Internet-of-Things}, Month = {oct}, Note = {Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.}, Series = {International Conference on the Internet of Things - IoT 2014}, Title = {{V}irtual {T}hings for {M}achine {L}earning {A}pplications:}, Pdf = {http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/wot-2014-virtual-things-for-machine-learning-applications.pdf}, Year = {2014}, Pdf = {http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/wot-2014-virtual-things-for-machine-learning-applications.pdf}, Bdsk-Url-2 = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2684432.2684434}} -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png) G. Bovet, A. Ridi, and J. Hennebert, “Appliance Recognition on Internet-of-Things Devices,” in 4th Int. Conf. on Internet of Things. IoT 2014 MIT, MA, USA., 2014.
G. Bovet, A. Ridi, and J. Hennebert, “Appliance Recognition on Internet-of-Things Devices,” in 4th Int. Conf. on Internet of Things. IoT 2014 MIT, MA, USA., 2014.
[Bibtex]@conference{bovet2014:iotdemo, author = "G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Antonio Ridi and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "Machine Learning (ML) approaches are increasingly used to model data coming from sensor networks. Typical ML implementations are cpu intensive and are often running server-side. However, IoT devices provide increasing cpu capabilities and some classes of ML algorithms are compatible with distribution and downward scalability. In this demonstration we explore the possibility of distributing ML tasks to IoT devices in the sensor network. We demonstrate a concrete scenario of appliance recognition where a smart plug provides electrical measures that are distributed to WiFi nodes running the ML algorithms. Each node estimates class-conditional probabilities that are then merged for recognizing the appliance category. Finally, our architectures relies on Web technologies for complying with Web-of-Things paradigms. ", booktitle = "4th Int. Conf. on Internet of Things. IoT 2014 MIT, MA, USA.", keywords = "Internet-of-Things, Machine Learning, Appliance Recognition, NILM, Non Intrusive Load Monitoring, HMM, Hidden Markov Models", note = "Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", title = "{A}ppliance {R}ecognition on {I}nternet-of-{T}hings {D}evices", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/iot-2014-appliance-recognition-on-internet-of-things-devices-demo-session.pdf", year = "2014", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “A Distributed Web-based Naming System for Smart Buildings,” in Third IEEE workshop on the IoT: Smart Objects and Services, Sydney, Australie, 2014, pp. 1-6.
G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “A Distributed Web-based Naming System for Smart Buildings,” in Third IEEE workshop on the IoT: Smart Objects and Services, Sydney, Australie, 2014, pp. 1-6.
[Bibtex]@conference{bovet:hal-01022861, author = "G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "Nowadays, pervasive application scenarios relying on sensor networks are gaining momentum. The field of smart buildings is a promising playground where the use of sensors allows a reduction of the overall energy consumption. Most of current applications are using the classical DNS which is not suited for the Internet-of-Things because of requiring humans to get it working. From another perspective, Web technologies are pushing in sensor networks following the Web-of-Things paradigm advocating to use RESTful APIs for manipulating resources representing device capabilities. Being aware of these two observations, we propose to build on top of Web technologies leading to a novel naming system that is entirely autonomous. In this work, we describe the architecture supporting what can be called an autonomous Web-oriented naming system. As proof of concept, we simulate a rather large building and compare the behaviour of our approach to the legacy DNS and Multicast DNS (mDNS).", address = "Sydney, Australie", booktitle = "Third IEEE workshop on the IoT: Smart Objects and Services", doi = "10.1109/WoWMoM.2014.6918930", isbn = "9781479947850", keywords = "iot, wot, smart building, web of things, internet of things", month = "Jun", pages = "1-6", title = "{A} {D}istributed {W}eb-based {N}aming {S}ystem for {S}mart {B}uildings", Pdf = "http://hennebert.org/download/publications/iotsos-2014-a-distributed-web-based-naming-system-for-smart-building.pdf", year = "2014", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png) G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Web-of-Things Gateways for KNX and EnOcean Networks,” in International Conference on Cleantech for Smart Cities & Buildings from Nano to Urban Scale (CISBAT 2013), 2013, pp. 519-524.
G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Web-of-Things Gateways for KNX and EnOcean Networks,” in International Conference on Cleantech for Smart Cities & Buildings from Nano to Urban Scale (CISBAT 2013), 2013, pp. 519-524.
[Bibtex]@conference{bovet2013:cisbat, author = "G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "Smart buildings tend to democratize both in new and renovated constructions aiming at minimizing energy consumption and maximizing comfort. They rely on dedicated networks of sensors and actuators orchestrated by management systems. Those systems tend to migrate from simple reactive control to complex predictive systems using self- learning algorithms requiring access to history data. The underlying building networks are often heterogeneous, leading to complex software systems having to implement all the available protocols and resulting in low system integration and heavy maintenance efforts. Typical building networks offer no common standardized application layer for building applications. This is not only true for data access but also for functionality discovery. They base on specific protocols for each technology, that are requiring expert knowledge when building software applications on top of them. The emerging Web-of-Things (WoT) framework, using well-known technologies like HTTP and RESTful APIs to offer a simple and homogeneous application layer must be considered as a strong candidate for standardization purposes. In this work, we defend the position that the WoT framework is an excellent candidate to elaborate next generation BMS systems, mainly due to the simplicity and universality of the telecommunication and application protocols. Further to this, we investigate the possibility to implement a gateway allowing access to devices connected to KNX and EnOcean networks in a Web-of-Things manner. By taking advantage of the bests practices of the WoT, we show the possibility of a fast integration of KNX in every control system. The elaboration of WoT gateways for EnOcean network presents further challenges that are described in the paper, essentially due to optimization of the underlying communication protocol.", booktitle = "International Conference on Cleantech for Smart Cities {{\&}} Buildings from Nano to Urban Scale (CISBAT 2013)", keywords = "IT for Sustainability, Smart Buildings, Web-of-Things, RESTful, KNX, EnOcean, Gateways", note = "Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", pages = "519-524", title = "{W}eb-of-{T}hings {G}ateways for {KNX} and {E}n{O}cean {N}etworks", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/cisbat-2013-web-of-things-gateways-for-knx-and-enocean-networks.pdf", year = "2013", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Energy-Efficient Optimization Layer for Event-Based Communications on Wi-Fi Things,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 19, pp. 256-264, 2013.
G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Energy-Efficient Optimization Layer for Event-Based Communications on Wi-Fi Things,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 19, pp. 256-264, 2013.
[Bibtex]@article{bovet:2013:ant:procedia, author = "G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "The Web-of-Things or WoT offers a way to standardize the access to services embedded on everyday objects, leveraging on well accepted standards of the Web such as HTTP and REST services. The WoT offers new ways to build mashups of object services, notably in smart buildings composed of sensors and actuators. Many things are now taking advantage of the progresses of embedded systems relying on the ubiquity of Wi-Fi networks following the 802.11 standards. Such things are often battery powered and the question of energy efficiency is therefore critical. In our research, we believe that several optimizations can be applied in the application layer to optimize the energy consumption of things. More specifically in this paper, we propose an hybrid layer automatically selecting the most appropriate communication protocol between current standards of WoT. Our results show that indeed not all protocols are equivalent in terms of energy consumption, and that some noticeable energy saves can be achieved by using our hybrid layer. ", doi = "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2013.06.037", issn = "1877-0509", journal = "Procedia Computer Science ", keywords = "Web-of-Things, RESTful services, WebSockets, CoAP, Energy efficiency, Smart buildings", note = "The 4th International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT 2013), the 3rd International Conference on Sustainable Energy Information Technology (SEIT-2013). Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", pages = "256-264", title = "{E}nergy-{E}fficient {O}ptimization {L}ayer for {E}vent-{B}ased {C}ommunications on {W}i-{F}i {T}hings ", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/ant-procedia-2013-energy-efficient-optimization-layer-for-event-based-communications-on-wi-fi-things.pdf", volume = "19", year = "2013", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “An Energy Efficient Layer for Event-Based Communications in Web-of-Things Frameworks,” in The 7th FTRA International Conference on Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering (MUE 2013), Springer – Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, 2013, vol. 240, pp. 93-101.
G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “An Energy Efficient Layer for Event-Based Communications in Web-of-Things Frameworks,” in The 7th FTRA International Conference on Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering (MUE 2013), Springer – Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, 2013, vol. 240, pp. 93-101.
[Bibtex]@inbook{bovet:2013:mue, author = "G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "Leveraging on the Web-of-Things (WoT) allows standardizing the access of things from an application level point of view. The protocols of the Web and especially HTTP are offering new ways to build mashups of things consisting of sensors and actuators. Two communication protocols are now emerging in the WoT domain for event-based data exchange, namely WebSockets and RESTful APIs. In this work, we motivate and demonstrate the use of a hybrid layer able to choose dynamically the most energy efficient protocol.", booktitle = "The 7th FTRA International Conference on Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering (MUE 2013)", doi = "10.1007/978-94-007-6738-6_12", isbn = "9789400767379", keywords = "Web-of-Things, RESTful services, WebSockets", month = "May", note = "Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", number = "3", pages = "93-101", publisher = "Springer - Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering", series = "Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering", title = "{A}n {E}nergy {E}fficient {L}ayer for {E}vent-{B}ased {C}ommunications in {W}eb-of-{T}hings {F}rameworks", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/mue-2013-an-energy-efficient-layer-for-event-based-communications-in-web-of-things-frameworks.pdf", volume = "240", year = "2013", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/external.png) G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Offering Web-of-things Connectivity to Building Networks,” in Proceedings of the 2013 ACM Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing Adjunct Publication, New York, NY, USA, 2013, pp. 1555-1564.
G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Offering Web-of-things Connectivity to Building Networks,” in Proceedings of the 2013 ACM Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing Adjunct Publication, New York, NY, USA, 2013, pp. 1555-1564.
[Bibtex]@conference{bovet2013:wot, author = "G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "Building management systems (BMS) are nowadays present in new and renovated buildings, relying on dedicated networks. The presence of various building networks leads to problems of heterogeneity, especially for developing BMS. In this paper, we propose to leverage on the Web-of-Things (WoT) framework, using well-known standard technologies of the Web like HTTP and RESTful APIs for standardizing the access to devices seen from an application point of view. We present the implementation of two gateways using the WoT approach for exposing KNX and EnOcean device capabilities as Web services, allowing a fast integration in existing and new management systems.", address = "New York, NY, USA", booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2013 ACM Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing Adjunct Publication", doi = "10.1145/2494091.2497590", isbn = "9781450322157", keywords = "building networks, enocean, gateways, knx, web-of-things", note = "Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", pages = "1555-1564", publisher = "ACM", series = "UbiComp '13 Adjunct", title = "{O}ffering {W}eb-of-things {C}onnectivity to {B}uilding {N}etworks", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/wot-2013-offering-web-of-things-connectivity-to-building-networks.pdf", year = "2013", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png) A. Ridi, N. Zarkadis, G. Bovet, N. Morel, and J. Hennebert, “Towards Reliable Stochastic Data-Driven Models Applied to the Energy Saving in Buildings,” in International Conference on Cleantech for Smart Cities & Buildings from Nano to Urban Scale (CISBAT 2013), 2013, pp. 501-506.
A. Ridi, N. Zarkadis, G. Bovet, N. Morel, and J. Hennebert, “Towards Reliable Stochastic Data-Driven Models Applied to the Energy Saving in Buildings,” in International Conference on Cleantech for Smart Cities & Buildings from Nano to Urban Scale (CISBAT 2013), 2013, pp. 501-506.
[Bibtex]@conference{ridi2013:cisbat, author = "Antonio Ridi and Nikos Zarkadis and G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Nicolas Morel and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "We aim at the elaboration of Information Systems able to optimize energy consumption in buildings while preserving human comfort. Our focus is in the use of state-based stochas- tic modeling applied to temporal signals acquired from heterogeneous sources such as distributed sensors, weather web services, calendar information and user triggered events. Our general scientific objectives are: (1) global instead of local optimization of building automation sub-systems (heating, ventilation, cooling, solar shadings, electric lightings), (2) generalization to unseen building configuration or usage through self-learning data- driven algorithms and (3) inclusion of stochastic state-based modeling to better cope with seasonal and building activity patterns. We leverage on state-based models such as Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) to be able to capture the spatial (states) and temporal (sequence of states) characteristics of the signals. We envision several application layers as per the intrinsic nature of the signals to be modeled. We also envision room-level systems able to leverage on a set of distributed sensors (temperature, presence, electricity consumption, etc.). A typical example of room-level system is to infer room occupancy information or activities done in the rooms as a function of time. Finally, building-level systems can be composed to infer global usage and to propose optimization strategies for the building as a whole. In our approach, each layer may be fed by the output of the previous layers. More specifically in this paper, we report on the design, conception and validation of several machine learning applications. We present three different applications of state-based modeling. In the first case we report on the identification of consumer appliances through an analysis of their electric loads. In the second case we perform the activity recognition task, representing human activities through state-based models. The third case concerns the season prediction using building data, building characteristic parameters and meteorological data.", booktitle = "International Conference on Cleantech for Smart Cities {{\&}} Buildings from Nano to Urban Scale (CISBAT 2013)", keywords = "IT for Sustainability, Smart Buildings, Machine Learning", note = "Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", pages = "501-506", title = "{T}owards {R}eliable {S}tochastic {D}ata-{D}riven {M}odels {A}pplied to the {E}nergy {S}aving in {B}uildings", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/cisbat-2013-towards-reliable-stochastic-data-driven-models-applied-to-the-energy-saving-in-building.pdf", year = "2013", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png) G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Le Web des objets à la conquête des bâtiments intelligents,” Bulletin Electrossuisse, vol. 10s, pp. 15-18, 2012.
G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Le Web des objets à la conquête des bâtiments intelligents,” Bulletin Electrossuisse, vol. 10s, pp. 15-18, 2012.
[Bibtex]@article{gerome2012:electrosuisse, author = "G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "L’am{\'e}lioration de l’efficacit{\'e} {\'e}nerg{\'e}tique des b{\^a}timents n{\'e}cessite des syst{\`e}mes automatiques de plus en plus sophistiqu{\'e}s pour optimiser le rapport entre les {\'e}cono- mies d’{\'e}nergie et le confort des usagers. La gestion conjointe du chauffage, de l’{\'e}clairage ou encore de la production locale d’{\'e}nergie est effectu{\'e}e via de v{\'e}ri- tables syst{\`e}mes d’information reposant sur une multi- tude de capteurs et d’actionneurs interconnect{\'e}s. Cette complexit{\'e} croissante exige une {\'e}volution des r{\'e}seaux de communication des b{\^a}timents.", issn = "1660-6728", journal = "Bulletin Electrossuisse", keywords = "wot, iot, green-it, it-for-green", note = "Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", pages = "15-18", title = "{L}e {W}eb des objets {\`a} la conqu{\^e}te des b{\^a}timents intelligents", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/electrosuisse-2012-le-web-des-objets-conquete-batiments-intelligents.pdf", volume = "10s", year = "2012", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png) G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Communicating With Things – An Energy Consumption Analysis,” in Pervasive, Newcastle, UK, 2012, pp. 1-4.
G. Bovet and J. Hennebert, “Communicating With Things – An Energy Consumption Analysis,” in Pervasive, Newcastle, UK, 2012, pp. 1-4.
[Bibtex]@conference{bove12:pervasive, author = "G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "In this work we report on the analysis, from an energy consumption point of view, of two communication methods in the Web-of-Things (WoT) framework. The use of WoT is seducing regarding the standardization of the access to things. It also allows leveraging on existing web application frameworks and speed up development. However, in some contexts such as smart buildings where the objective is to control the equipments to save energy, the underlying WoT framework including hardware, communication and APIs must itself be energy efficient. More specifically, the WoT proposes to use HTTP callbacks or WebSockets based on TCP for exchanging data. In this paper we introduce both methods and then analyze their power consumption in a test environment. We also discuss what future research can be conducted from our preliminary findings.", address = "Newcastle, UK", booktitle = "Pervasive", keywords = "web-of-things; smart building; RESTful services; green-computing", month = "June", note = "Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", pages = "1-4", title = "{C}ommunicating {W}ith {T}hings - {A}n {E}nergy {C}onsumption {A}nalysis", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/pervasive-2012-communicating-with-things-an-energy-consumption-analysis.pdf", year = "2012", } -
![[PDF]](https://icosys.ch/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png) C. Gisler, G. Barchi, G. Bovet, E. Mugellini, and J. Hennebert, “Demonstration Of A Monitoring Lamp To Visualize The Energy Consumption In Houses,” in The 10th International Conference on Pervasive Computing (Pervasive2012), Newcastle, 2012.
C. Gisler, G. Barchi, G. Bovet, E. Mugellini, and J. Hennebert, “Demonstration Of A Monitoring Lamp To Visualize The Energy Consumption In Houses,” in The 10th International Conference on Pervasive Computing (Pervasive2012), Newcastle, 2012.
[Bibtex]@conference{gisl12:pervasive, author = "Christophe Gisler and Grazia Barchi and G{\'e}r{\^o}me Bovet and Elena Mugellini and Jean Hennebert", abstract = "We report on the development of a wireless lamp dedicated to the feedback of energy consumption. The principle is to provide a simple and intuitive feedback to residents through color variations of the lamp depending on the amount of energy consumed in a house. Our system is demonstrated on the basis of inexpensive components piloted by a gateway storing and processing the energy data in a WoT framework. Different versions of the color choosing algorithm are also presented.", address = "Newcastle", booktitle = "The 10th International Conference on Pervasive Computing (Pervasive2012)", keywords = "Web of Things; Energy feedback; Green Computing; IT-for-Green", month = "jun", note = "Some of the files below are copyrighted. They are provided for your convenience, yet you may download them only if you are entitled to do so by your arrangements with the various publishers.", title = "{D}emonstration {O}f {A} {M}onitoring {L}amp {T}o {V}isualize {T}he {E}nergy {C}onsumption {I}n {H}ouses", Pdf = "http://www.hennebert.org/download/publications/pervasive-2012-demonstration-of-a-monitoring-lamp-to-visualize-the-energy-consumption-in-houses.pdf", year = "2012", }

