
Neural Machine Translation (NMT) engines have revolutionized the field of machine translation in just a few years. Translation engines such as Google Translate or DeepL have reached very fine performance levels on texts of a general nature. In specific contexts, translations are becoming increasingly technical and NMT engines need to undergo specialization through retraining based on contextualized data.That is why Hieronymus AG has created LexMachina, the first NMT engine specializing in the translation of legal and financial texts. Its target users include law firms, banks, (re)insurance companies, consultants and the big4, in Switzerland and Germany. Such companies will benefit from higher quality custom-made NMT engines, with a shorter set-up time.
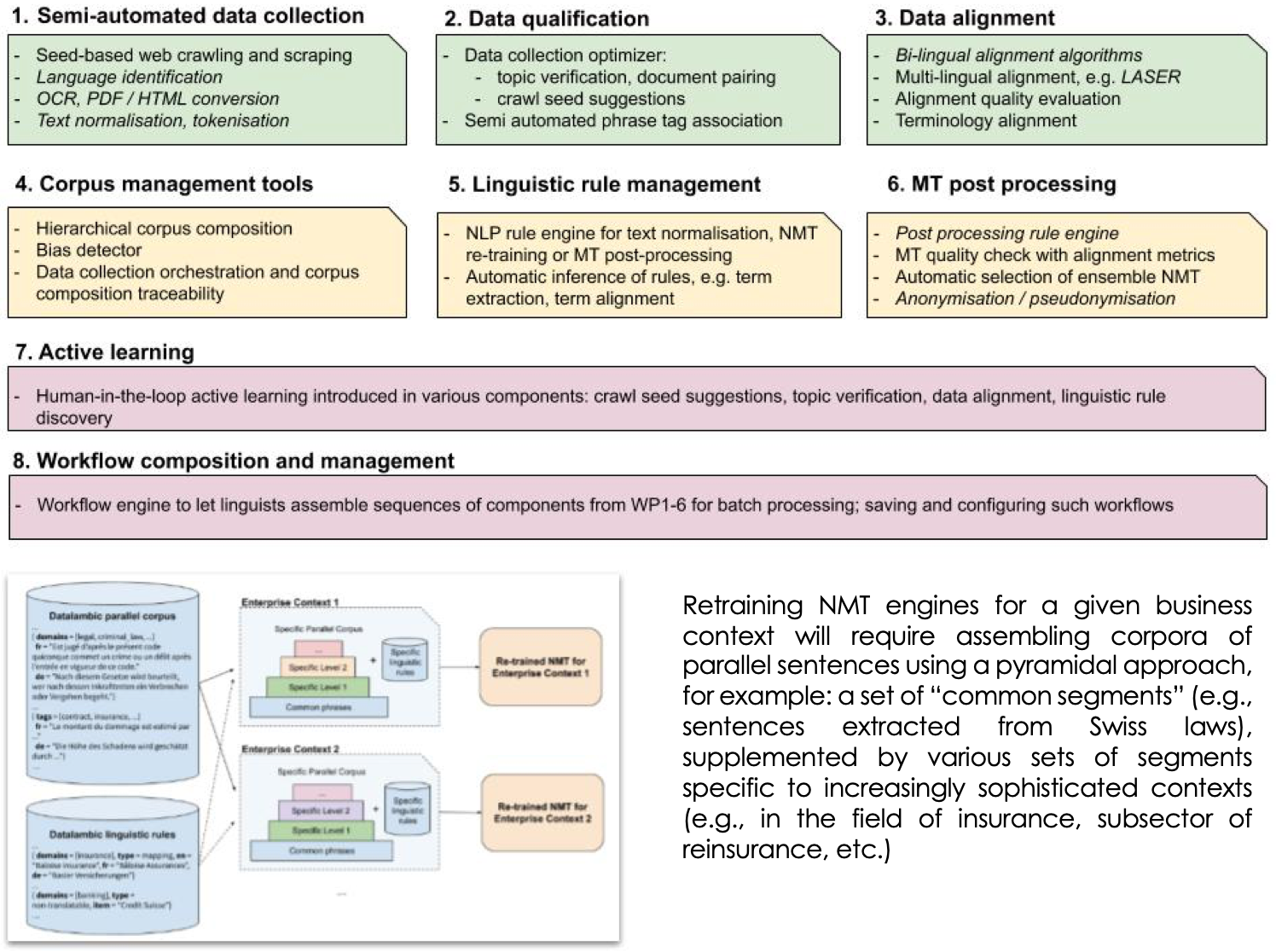
The purpose of the Datalambic Project, carried out in partnership with iCoSys, is to create a tool ecosystem for semi-automated collection, preparation and correction of high-quality data in order to (re)train neural translation engines in the desired specialization(s), including looped feedback from linguists, lawyers and users. The ecosystem will be modular, including: context-targeted web scraping, document classification, multilingual sentence alignment, term extraction, pseudonymization and customized machine translation post-processing.
In 2021, our project was selected to be features in the framework of the 125 years of the engineering school of Fribourg. A movie explaining the project was created and here is the result.
In July-August 2022, Datalambic ended with strong successful realisation, leading to the creation of a spin-off by Hieronymus called Neur.on. The spin-off will continue with our findings in the project and could convince investors to carry-on the company with an investment round of 1.6 MCHF. See the cover in our news Section: https://icosys.ch/artificial-intelligence-for-law and also on StartupTicker.
Here is a picture of the end-of-project team.

